ENVIRONMENT
▪︎ Environmental Management Vision

▪︎ Environmental Management Policy
| KISCO recognizes environmental conservation as a corporate social responsibility and has acquired the global standard certifications ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 for environmental management and occupational health and safety management systems. Based on this, we established and implemented environmental management strategies and detailed action plans for all stages of product development, production and use. |
|---|
| 1. Recognizing that environmental protection is a basic social responsibility of a company, KISCO complies with 1. all laws and regulations on environmental protection. 2. Company-wide efforts are made to continually improve environmental protection systems. 3. In the entire process of product development, production and use, we do our best to develop technologies that 3. consider environmental preservation. 4. We ensure that we are not complicit in human rights abuses. 5. We provide and actively support environmental education and opportunities for employees to improve 5. their awareness of environmental preservation. |
|---|
|
KISCO has established an integrated “KISCO HSE Management Policy” based on ISO 14001 and ISO 45001.
|
|---|
▪︎ Investment for the Environment
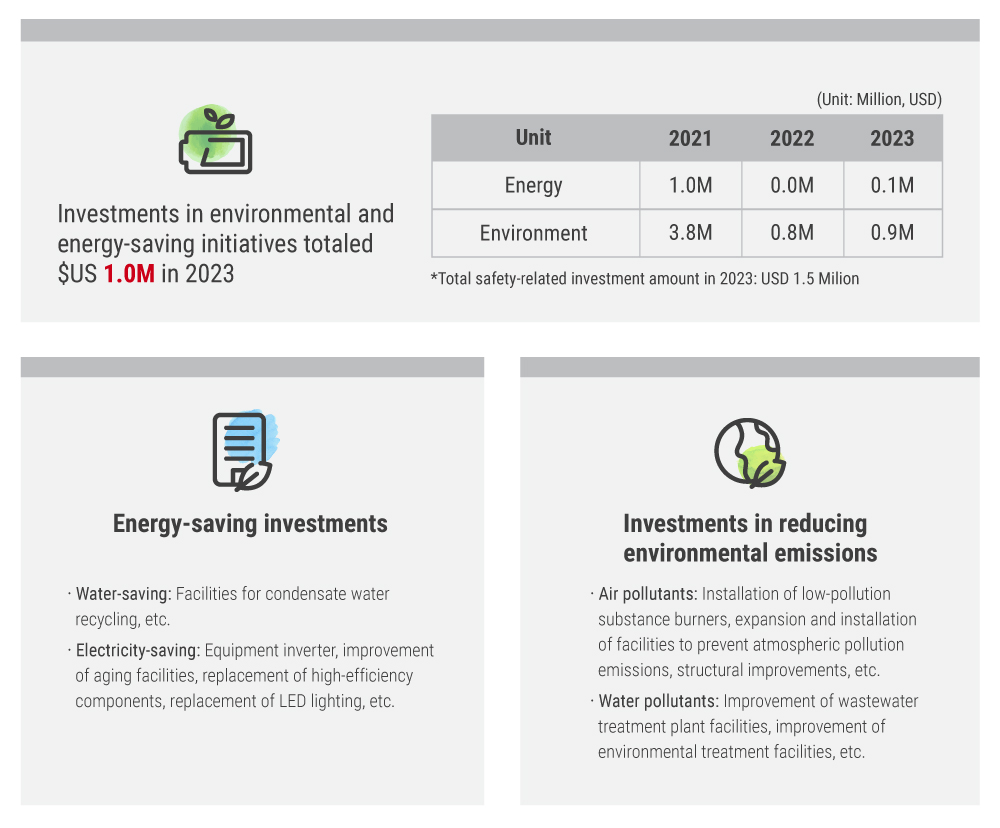
| KISCO pursues sustainable environmental management through various activities aimed at reducing environmental impact. We continuously invest in environmental and energy-related initiatives to reduce resource and energy consumption during product manufacturing and to minimize pollutant emissions. |
|---|
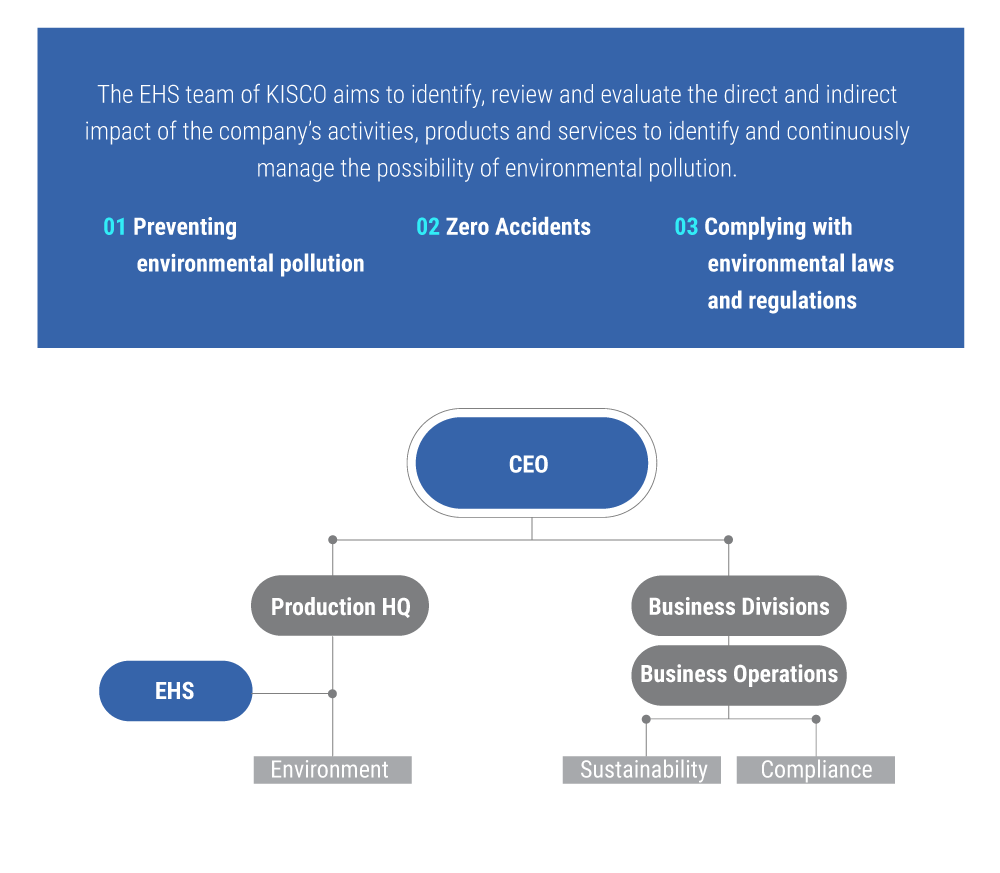
▪︎ EHS Organisation
▪︎ Environmental Performance Management System:
▪︎ Certification Status related to Sustainable Management/ESG
| In addition to the global standard certifications ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 for environmental and occupational health and safety management, KISCO has sustainability certifications applicable to each industry that we work in. We incorporate these regulations into our management practices for sustainable management. |
|---|
| Certificate | Site | First certification year | Certified by |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 Quality Management System |
All site | 2005 | Lloyd’s Register Quality Assurance Limited |
| ISO 14001 Environmental Management System |
KIF1, KIF3, KIF4 | 2005 | Lloyd’s Register Quality Assurance Limited |
| ISO 45001 Occupational health and Safety Management System |
KIF1, KIF3, KIF4 | 2005* | Lloyd’s Register Quality Assurance Limited |
| Bluesign System bluesign® System Partner Solutions and services for sustainable textile industry |
KIF1, KIF3, KIF4 | 2010 | bluesign Technologies ag |
| Global Organic Textile Standard | KIF1, KIF3, KIF4, KIF5 | 2008 | Ecocert Group |
| ECO Passport by OEKO-TEX® Certification system for chemicals, colorants and auxiliaries used in the textile industry |
KIF5 | 2020 | TESTEX AG |
| GreenGuard Indoor Air Quality Safety Certification |
KIF5 | 2023 | UL Solutions |
| FSSC 22000 Food Safety Management Systems |
JMC | 2018 | SGS United Kingdom Ltd. |
| HAS23000 Halal Assurance System |
JMC | 2020 | Fatwa Commission of MU |
*OHSAS 18001 initial certification year, transition from OHSAS 18001 to ISO 45001 successfully passed in 2021.
※ KIF: Kyung-In Factory. Incheon Factory (KIF1, KIF2)/ Ansan Factory (KIF3)/ Sihueung Factory (KIF4,KIF5)/ Iksan Factory (KIF6)/ Yesan Factory (KIF7)
▪︎ Status of environmental management education
| KISCO enhances employees’ environmental management awareness and conducts specialized environmental management training tailored to job roles to strengthen environmental risk management and prevent accidents. |
|---|
| Category | Frequency | Training hour | Target of training | Completion count |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training for air quality management technology | 3 years | 28 hours | Safety management person | 5 |
| Training for water quality management technology | 3 years | 28 hours | Safety management person | 2 |
| Education for hazardous chemical substance managers | 2 years | 16 hours | Hazardous chemicals manager | 16 |
| Education for hazardous chemical substance handlers | 2 years | 16 hours | Hazardous chemicals handler | 121 |
| Education for workers handling hazardous chemicals | Annual | 2 hours | Handling of hazardous chemicals | 102 |
*Number of course completions in 2023.
▪︎ Environment Management laws/regulations and environmental accident response
| To respond to strengthening environmental regulations, both domestically and internationally, KISCO has established dedicated teams for each area and continuously monitors all related laws and regulations, as well as guidelines from various domestic and international government and private initiatives. KISCO has established procedures to comply with these regulations and introduced management systems to manage each item. |
|---|
| Management areas | Laws/regulations | Department in charge |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental management | Air Conservation Act, Water Conservation Act, etc. | EHS |
| Substance management | Chemical Control Act, Industrial Safety and Health Act, etc. | Compliance, Sustainability |
| Health and safety management | Major Accidents and Disasters Countermeasures Act, Occupational Safety and Health Act, etc. |
Safety |
| ▪︎ Monitoring status of laws/regulations |
|---|
 |
 |
|---|
▪︎ Environment Management System
| KISCO has obtained ISO 14001 certification, a global standard certification for environmental management systems, at some of its facilities and has established the integrated ‘KISCO Safety, Health, and Environment Management Policy’. This policy is deployed across all facilities. We also operate environmental monitoring systems and chemical management systems to efficiently monitor energy resources, pollutants, chemicals and other environmental-related aspects and to manage environmental risks in real-time. |
|---|
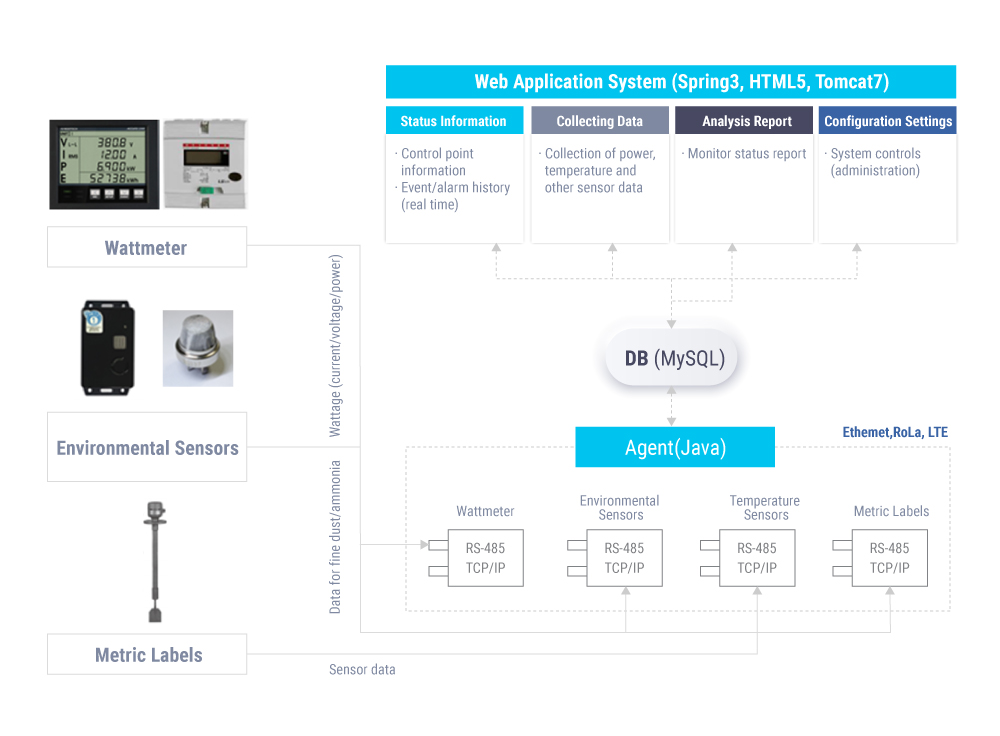
| ▪︎ Environment Management System KISCO manages environmental impacts by adopting various systems such as monitoring environmental substances, managing chemical substances, complying with regulations and carrying out environmental impact assessments. A key tool for managing our data is our Environmental Management System (EMS). The system enables real-time measurement-based monitoring of energy resources and data through a network of environmental sensors. The system is underpinned by an integrated environmental monitoring system that includes monitors for electricity and air quality. – Real-time measurement-based monitoring of energy resources and data through a network of environmental sensors. – Integrated environmental monitoring system that includes monitors for electricity and air quality |
|---|
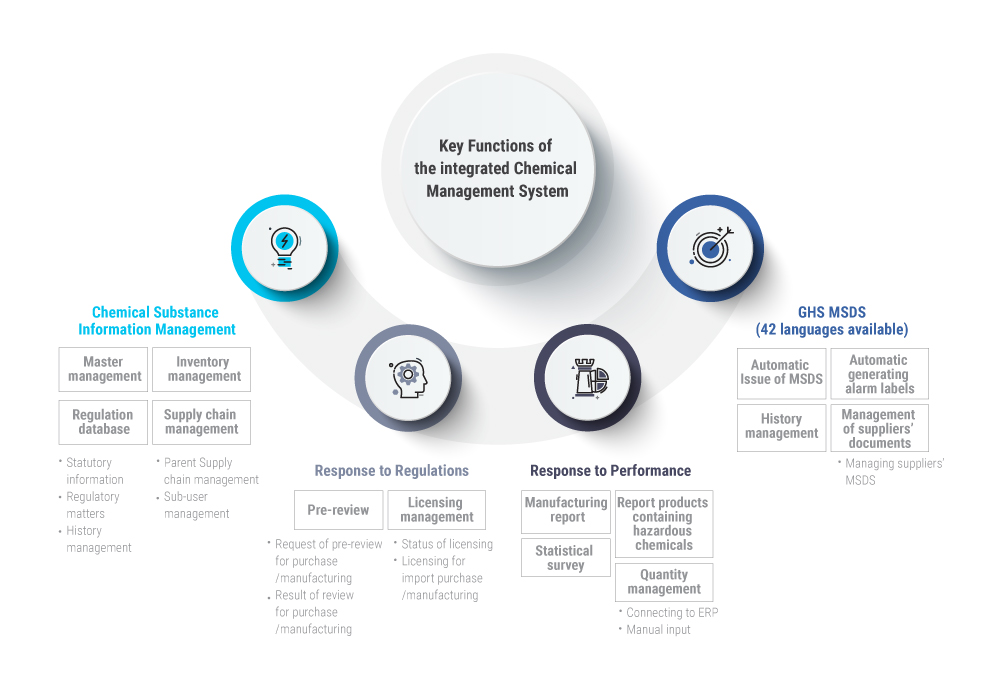
| ▪︎ Chemical Substances Management System KISCO’s electronic Chemical substances Management System (eCMS) is a substance management and regulation database. It includes over 40,000 domestic and 400,000 overseas-registered chemical substances. It assists compliance with 15 environmental safety regulations including the Korean Chemical Evaluation Act, the Korean Chemicals Act, the Industrial Safety Act and similar regulations in 47 other countries. The system enables the proactive review of information related to purchase, manufacturing, handling, licensing, performance management and partnering. The system also has an integrated MSDS inventory management module. |
|---|
| ▪︎ Environmental Impact Assessment Management – ISO 14001 The environmental team of KISCO established a process to conduct initial, regular and random environmental impact assessments according to the following procedures. Following the audits, corrective actions are initiated if any activities deviate from internal regulations. 1) Evaluation of internal and external issues and stakeholder requirements 2) Evaluation of process, environmental aspects, environmental impacts and materiality issues 3) Air, water quality, waste, noise/vibration, odor, soil contamination, resource/energy consumption audits |
|---|
▪︎ Supply Chain Risk Management
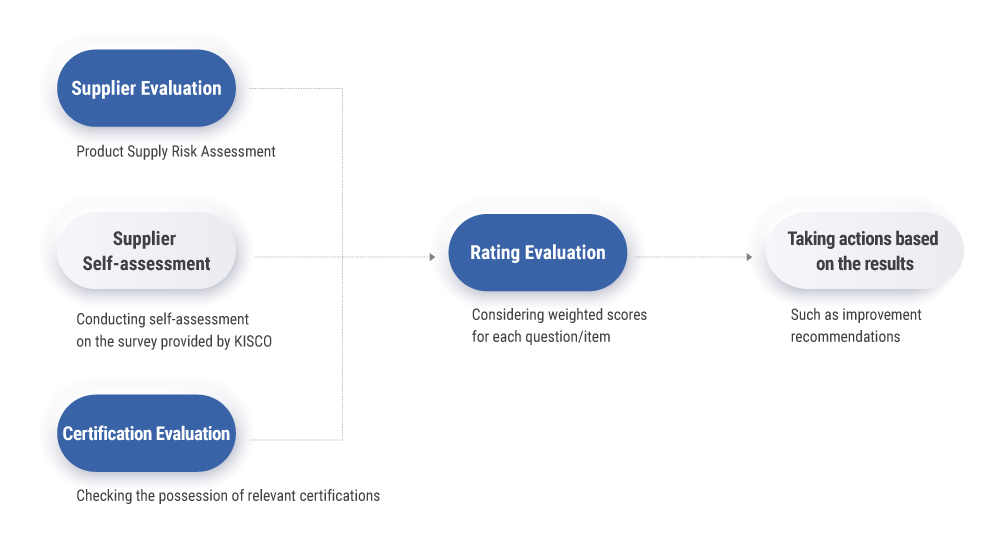
| KISCO is striving to grow together based on collaboration with suppliers, emphasizing human rights and the environment, and building a sustainable supply chain. With the goal of recognizing and managing the transparency of the supply chain, we are enhancing supply chain ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) risks by supplementing diagnostic items for non-financial risks such as human rights and the environment, in addition to risk factors related to product supply such as finance and quality. We have established a supplier code of conduct and demand compliance from our suppliers. |
|---|
| ▪︎ Supply Chain Risk Management Process ▪︎ We utilize a multi-assessment approach to ensure the transparency of diagnostics. ▪︎ We will make continuous efforts to build a more responsible supply chain through ongoing process enhancement. |
|---|
| ▪︎ Supplier Code of Conduct |
|---|
| Download Supplier Code of Conduct |
▪︎ Environmental Impact Management
| KISCO formulates strategies and plans for issues related to the environment such as energy, water resources, pollutants and resource circulation. This is in response to the climate crisis and to minimize business risks caused by environmental impacts on our product manufacturing processes. We manage performance accordingly. |
|---|
▪︎ Pollutant Management
| ▪︎ GHG Emissions In Korea, renewable energy sources currently account for less than 10% of electricity generation and the government has targets to increase this to 21.6% by 2030. For GHG emissions, the Korean government targets are a 40% reduction by 2030 and 100% by 2050 (based on a 2018 baseline). As mechanisms become available, KISCO plans to contract increasing amounts of renewably generated electricity. In line with the implementation of a GHG emission trading system in Korea, KISCO manages carbon emissions based on the revised guidelines: “Reporting and Certification of Greenhouse Gas Emission Trading System (No. 2021-10)” published by the Korean Ministry of Environment. These guidelines are based on those published as part of IPCC 2006. |
|---|
▪︎ Air Pollutant Emissions: NOx, SOx, Dust Through the Air Environment Conservation Act the Korean Government has established targets for the emission of air pollutants such as Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), Sulfur Oxides (SOx) and dust. KISCO has set internal control limits that are well below these levels. KISCO has also established processes for identifying excess emissions and for taking corrective actions in case emissions are found to exceed internal management standards. RTO and HTO facilities have been installed to reduce pollutants discharged into the atmosphere and prevent air pollution. Since 2019 KISCO has achieved reductions in SOx and dust emissions through a combination of new facilities and process improvements. |
|---|
▪︎ Water Emissions: COD, BOD, SS In order to contol the emission of water pollutants from production activities, KISCO records data for Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Suspended Solids (SS). Our in-house targets are more strict than required by regulations or standards that apply to our production. All water used in production processes is discharged through our own wastewater treatment facilites or local, joint treatment facilities. Water quality is continuously evaluated and managed. |
|---|
▪︎ KISCO Resource Circulation
| KISCO reviews the recycling of waste resources, such as byproducts and waste materials, that are generated during manufacturing processes. We aim to expand the practice of resource circulation through continued reuse and recycling of waste resources. |
|---|
| ▪︎ Process for reviewing waste recycling |
|---|
| ▪︎ Cases of waste recycling ▪︎ * Recycling of by-products from manufacturing processes ▪︎ – Reuse of reverse osmosis water generated during manufacturing processes: 5 tons/day (KIF6) ▪︎ – Reuse of waste acids as neutralizing agents in wastewater treatment: 3 tons/month (KIF6) ▪︎ – Reuse of waste acids as raw materials in manufacturing processes (KIF7) ▪︎ * Development of waste recycling applications ▪︎ – Reuse of 40% of incinerated waste organic solvents through collaboration with recyclable companies (KIF6) ▪︎ – 100% recycling of previously landfill-disposed acids through development of recycling applications (KIF6) |
|---|
▪︎ Environmental Impact Management Activities: Management of Air Pollutants
| KISCO establishes internal management standards that are more stringent than the legal emission standards and continues to invest in facilities to prevent air pollution, aiming to minimize the emission of air pollutants. |
|---|
| ▪︎ Investment in Air Pollution Prevention and Energy Conservation Facilities – RTO, HTO |
|---|
| In order to prevent air pollution and to enable energy savings through the reuse of waste heat, RTO (Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer) and HTO (Heat Transfer Oxidizer) facilities have been installed. These facilities reduced hydrocarbon emissions by 99.9% and save approximately 50% of energy usage for heating by utilizing recovered waste heat. |
|---|
| – Investment in RTO and HTO Facilities – Status of Thermal Oxidation Facilities |
|---|
 |
|
| ※ KIF: Short for Kyung-In Factory Incheon Factory (KIF1, KIF2)/ Ansan Factory (KIF3)/ Siheung Factory (KIF4, KIF5)/ Iksan Factory (KIF6)/ Yesan Factory (KIF7) |
|---|
| ▪︎ Environmental impact target and performance management ▪︎ – Management of pollutant discharge after installation of KIF4 HTO ▪︎ |
|---|
Classification | Before installation | Management objective | 2022 | 2023 |
Reduction rate of | 70.0% | 99.0% | 99.9% | 99.9% |
▪︎ Environmental Impact Management Activities: Management of Water Pollutants
| To minimize the discharge of water pollutants, KISCO establishes and manages more stringent internal management standards than the legal discharge limits specific to each area where its facilities are located. Recycled water is used in many areas and some domestic facilities have their own wastewater treatment plants. |
|---|
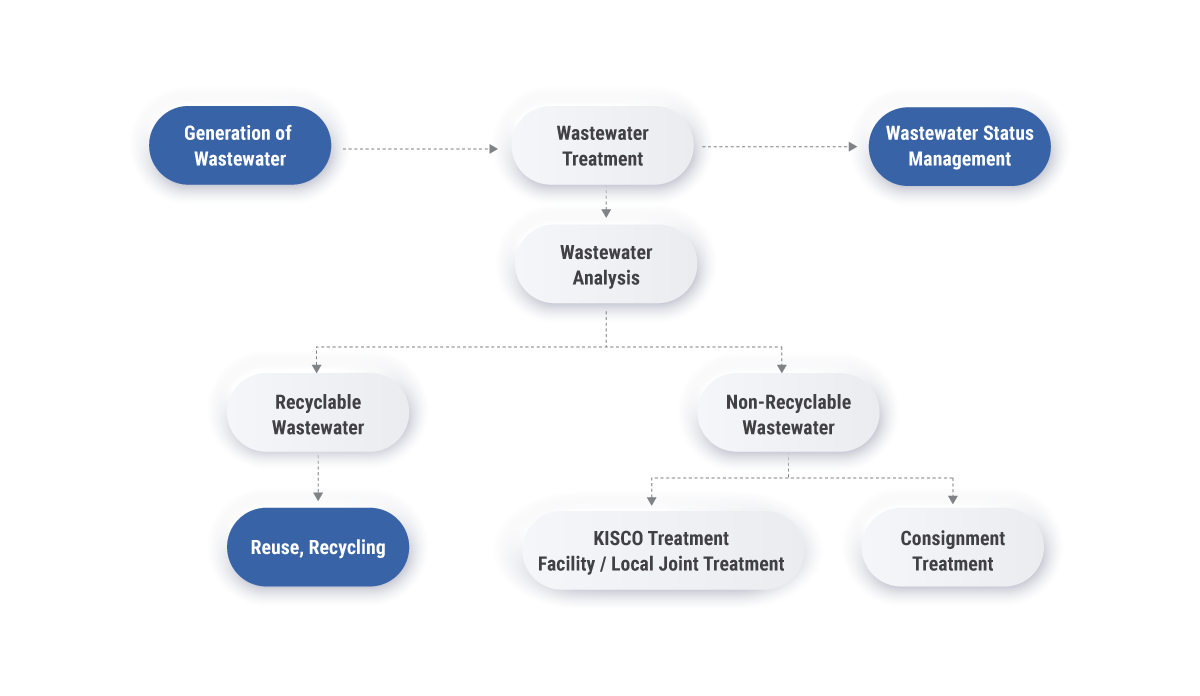
| ▪︎ Wastewater Treatment Facilities KISCO has its own wastewater treatment facilities in 3 of the 7 domestic factories in Korea. The other factories use local, joint wastewater treatment or consignment of waste treatment depending on the region and the type of wastewater. In order to reduce wastewater generation and water usage, KISCO continues to make efforts to reuse and recycle wastewater through self-treatment or consignment treatment. |
|---|
| ▪︎ Wastewater Treatment Facilities Process |
|---|
 |
 |
▪︎ Environmental data management
| ▪︎ GHG (t-CO2 eq) Emission Management |
|---|
|
|---|
| – The national criteria based on the Ministry of Environment’s notification “Guidelines for Reporting and Certification of Greenhouse Gas – Emissions Trading under the Greenhouse Gas Emissions Trading System (Ministry of Environment Notification No. 2021-10) – The aforementioned greenhouse gas emissions refer to the total emissions aggregated from the domestic business sites of KISCO, and neither – the aggregated emissions nor individual sites are subject to the Ministry of Environment’s greenhouse gas emissions trading system. – The update reflects the reclassification for Scope 1/2 and the use of some renewable energy sources. 1) Scope 1: Carbon emissions potentially generated during the manufacturing process of LNG, gasoline, diesel, and the company’s products, 1) calculated based on chemical formulas. 2) Scope 2: Calculated based on the supplier’s invoices for electricity and steam usage. 3) Emissions intensity = Total greenhouse gas emissions / Total revenue. |
|---|
| ▪︎ Air/water pollutant emissions management |
|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1) Based on data submitted to the Korean Government Stack Emission Management System (SEMS) or self-measurement records measured 1) by an external company. The total emissions for each domestic factory are summed – – Self-measurement record (measurement of external companies) standard for workplaces with less than 3 types (KIF3,5,6,7) that are not – – subject to SEMS input 2) Based on data summed and submitted to the Korean National Pollutant Survey (water quality) and the total emissions of KISCO notified 2) by the wastewater plant or consignment treatment company – – Wastewater facilities, or with self-measurement records based on the data submitted to the Korean National Pollutant Survey – – Discharge water after treatment at a joint treatment facilities in the area 3) From 2022, the nationwide pollution source survey (water quality) management item will be changed from COD to TOC and reflected 3) in our management item. – – Errors were found in the calculation details of the existing posted content on water pollution substances, and it has been corrected. 4) The total discharge volume of each domestic business site of Kyeongin Yanghang, as notified by the submitted data from the nationwide pollution 4) source survey (water quality) and by the joint or consigned treatment facilities: – – For businesses with wastewater treatment facilities and self-measurement record books, based on the submitted data from the nationwide pollution – – source survey. – – For businesses with joint or consigned treatment facilities, based on the data provided in the notification. |
|---|
| ▪︎ Waste Management by Disposal Method |
|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Figures based on data submitted to Korean government system and from recycling companies * Recycled waste rate = recycled waste/total waste * We have updated the type classification errors and missing data from the existing posted content. |
|---|
▪︎ Energy and Water Resource Usage Reduction Activities
| KISCO practices energy efficiency improvements for climate change adaptation, investing in facilities to reduce energy usage, implementing smart eco-factory projects, and conducting campaigns for household energy and water usage reduction. In addition, it sets energy and water resource reduction targets for each facility based on production plans, establishes activity plans for reduction, and manages performance accordingly. Some facilities also use recycled steam for all steam required for manufacturing. |
|---|
| ▪︎ Environmentally Friendly Vehicle Ownership Ratio: 27% |
|---|
| – | Based on corporate-owned or registered vehicles (including registered forklifts). |
|---|---|
| – | Environmentally friendly vehicle ownership ratio: 18 out of 66 vehicles are electric or hybrid cars. |
| ▪︎ External Wall Insulation |
|---|
| KISCO has implemented insulation on its exterior walls, resulting in an annual energy saving of 38,089 kWh for heating and cooling needs. |
|---|
Item | Before installation | Objective | 2022 | 2023 |
Effectiveness of external wall insulation construction | - | 23.6tCO2e | 17.5tCO2e | 23.8tCO2e |
| Before construction | After construction |
 |
 |
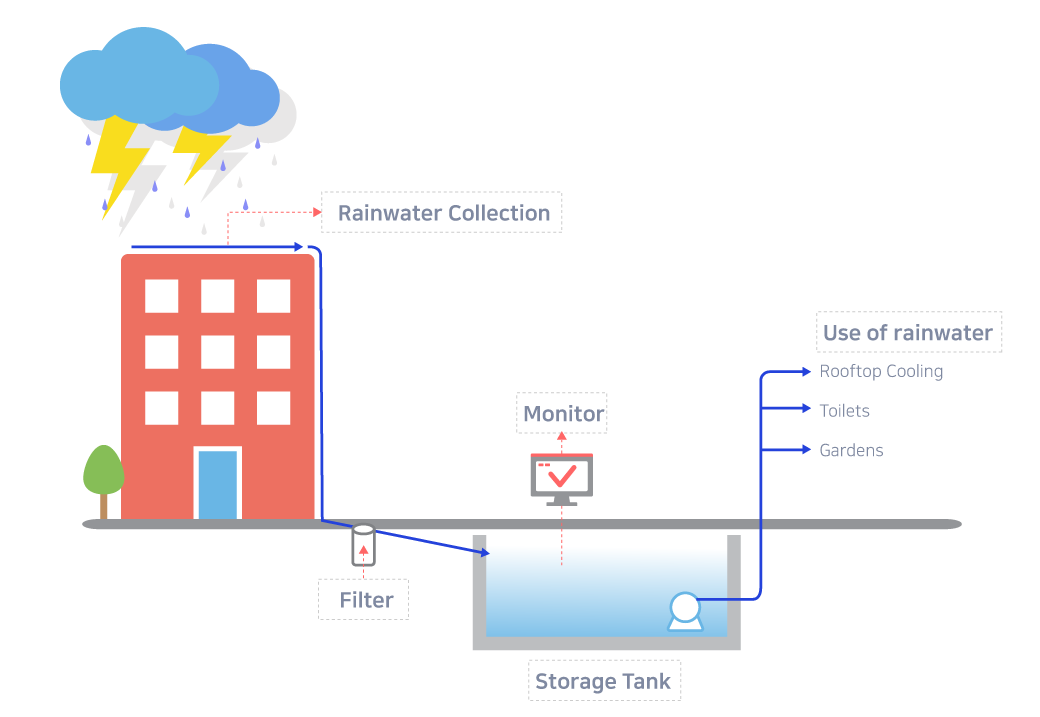
| ▪︎ Rainwater Harvesting |
|---|
| Through the Smart Eco-Factory project, KISCO converted sewage treatment facilities into rainwater utilization facilities. Collected rainwater was then used for production processes, thereby reducing the consumption of tap water. |
|---|
Item | Before installation | Objective | 2022 | 2023 |
Outstanding recycling performance | - | 268.7㎥ | 312.0㎥ | 272.0㎥ |
* The amount of rainwater reused in 2023 was 272.0㎥, achieving 101.2% of the plan (268.7㎥).
 |
 |
| ▪︎ LED Light Replacement |
|---|
| KISCO is replacing installed lighting in each facility with LEDs, which can reduce power consumption by 40% compared to conventional metal halogen lights. |
|---|
 |
 |
| ▪︎ In-house energy saving campaign |
|---|
| – | Office temperature maintenance campaign (26-28ºC in summer / 18-20ºC in winter) |
|---|---|
| – | Power off campaign for unused equipment during absence |
| – | Efficiency improvement activities through regular equipment overhaul management |
| – | Utility usage reduction activities by business site |
 |
▪︎ Energy usage management
| Sort | Unit/Year | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total energy consumption | TJ | 608 | 580 | 518 |
| Unit¹⁾ | TJ/10 mil KRW | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| In-house Energy Usage Targets | TJ | 549 | 562 | 521 |
| (Achievement Rate of Targets) | % | 69 | 79 | 84 |
| Energy Consumption Management²﹚ | TJ | 43 | 45 | 40 |
| (Renewable energy usage ratio) | % | 7 | 8 | 8 |
* Calculations are based on the Korean Ministry of Environment Notice “Guidelines for Reporting and Certification of Emissions of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
– Trading System (Ministry of Environment Notice) (No. 2021-10)”.
* The above greenhouse gas emissions are the sum of the total emissions limited to the domestics business sites of KISCO and are not subject to
– the greenhouse gas emission trading system of the Korean Ministry of Environment.
* We have updated the previous post to include the missing data.
– 1) Unit: Energy Usage Total Emissions / Total Revenue
– 2) The amount of energy from renewable sources provided by the supplier
▪︎ Water usage management
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1) Based on the water bill issued per business location 1)– Incheon (KIF1, KIF2) / Gyeonggi (KIF3, KIF4, KIF5) / Iksan, Yesan (KIF6, KIF7) / Seoul Office (Office building, Research institute). |
|---|
▪︎ Eco-friendly certification and initiative activities
| As a member of the Global Green Certification and Related Initiative, we design and produce environmentally friendly and secure products. |
|---|
Eco-friendly Certification
|
▪︎ bluesign® |
|
|---|---|
| KISCO has been certified as a bluesign® system partner since 2010. The bluesign® system is a sustainable certification system for the entire textile industry supply chain. The system oversees and manages production processes for five key areas: corporate resource productivity, consumer safety, air pollution, water pollution, and work health and safety, and independent audits identify improvements and validate processes. Over 200 of our textile dye products have been approved by bluesign®. More detailed information can be found via the link below https://www.bluesign.com/en |
 |
|
▪︎ GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) |
|
|---|---|
| The goal of GOTS is to define the requirements that organic textile products must meet, ensuring the safe use of textile products by ensuring that the entire process is environmentally and socially responsible from harvesting raw materials to final labeling. Our company has received GOTS certification for over 150 dye and ink products. KISCO’s compliance with GOTS is certified by ECOCERT. More information can be found via the link below. https://global-standard.org/ |
 |
|
▪︎ ECO PASSPORT by OEKO-TEX® |
|
|---|---|
| ECO PASSPORT BY OEKO-TEX® is a chemical, dye and additive certification used in textile and leather production. This means that they are responsible for production and handling chemicals to protect people and the environment, and our certified dye and ink products are proof that they are suitable for sustainable textile production. Our company has passed the certification standard for over 40 ink products. More information can be found via the link below. https://www.oeko-tex.com/en/our-standards/oeko-tex-eco-passport |
 |
|
▪︎ Green Guard |
|
|---|---|
| GREENGUARD Certification is an environmentally friendly certification program issued by UL, a global safety standard certification organization, for indoor air quality. It evaluates and certifies various products such as building materials, office furniture, and electronic products to ensure compliance with indoor environmental and air quality standards. It rigorously measures the emission levels of volatile organic compounds, formaldehyde, respirable particles, and other substances that can cause allergies, respiratory disorders, and neurological disorders. Our UV ink product has passed the GREENGUARD Gold Certification standard, and you can find more details at the following link. https://www.ul.com/services/ul-greenguard-certification |
 |
Initiative Activities
|
▪︎ ZDHC |
|
|---|---|
| The ZDHC (Zero Discharge Hazardous Chemicals) Foundation is a cooperative organization composed of brands, factories, chemical manufacturers and certification bodies, aimed at minimizing environmental pollution throughout the textile industry and improving sustainable chemical management within the supply chain. Managing harmful substances in the manufacturing process is essential, and the foundation operates various programs to integrate regulatory targets and levels to apply them on-site. KISCO has been an active ZDHC Signatory Chemical Formulator since 2019. Over 400 of our dye and ink products comply with both product hazard and production environmental assessment criteria and are registered on the ZDHC Gateway. Further information can be found via the following link. https://www.roadmaptozero.com/ |
 |
|
▪︎ SCTI |
|
|---|---|
| SCTI (Sustainable Chemistry for Textile Industry), launched in 2020, is an alliance of leading chemical companies that aims to enable the textile and leather industries to apply cutting-edge sustainable chemical solutions to protect factory workers, local communities, consumers, and the environment. Our company, along with Archroma Textile Effects, CHT Group, Pulcra Chemicals, Rudolf Group, and Tanatex Chemicals, is a founding member of SCTI. SCTI and its members are collaborating with bluesign® to develop the Sustainable Chemistry Index, a sustainability index for products and companies. More information is available via the link below. https://scti.org/ |
 |
▪︎ Environmentally-friendly sales performance
| Item | Unit/Year | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmentally Friendly Sales | 10 million won | 13,452 | 12,890 | 11,870 |
| Environmentally Friendly Sales Ratio | % | 49 | 52 | 55 |
* Yearly sales performance of products certified by third-party environmental certifications such as GOTS and ECO-PASSPORT
– The list of certified products may vary by year, and sales performance is calculated based on products certified in each respective year.
* Environmentally Friendly Sales Ratio = Environmentally Friendly Sales / Total Sales of KISCO